The Raritan Blog
Home » Raritan Blog » Types of Data Center Cooling Techniques
Types of Data Center Cooling Techniques
Rick Gonedes
November 1, 2017
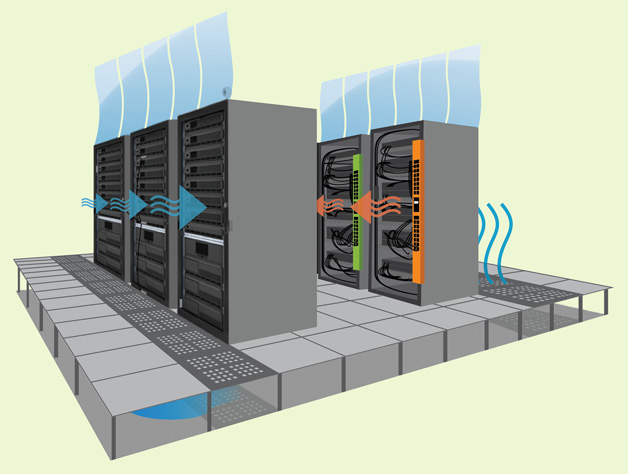
Having proper temperature management in your data center is absolutely vital to maintain the functionality of the equipment. Having an excess of warm air and humidity within your data center can create a financial burden for your business that can be avoided. In this guide, you will become more knowledgeable on the types of cooling techniques that you can implement in your data center.
Free Cooling
Free cooling is a cost-effective way to ensure that your data center’s temperature flow is properly functioning. When this technique is used, the cooling used is minimalistic and reduces the overall expenditures for cooling. This method consists of two systems known as air-side economization and water-side economization. Air-side economization uses air from the outdoors to regulate the equipment’s coolness. This technique has its flaws since it can potentially allow pollutants and moisture from the outdoors to enter the data center.
Chilled Water System
Liquid cooling can be more efficient and direct in its cooling techniques. This is due to the fact that chilled water can be directly targeted to the desired area, without it being necessary to supply cool air to all areas of the facility. With the chilled water technique, the CRAH is connected to a chiller. As the chilled water travels through coils, it engulfs the heat and deposits it into the chiller. Once the water returns to the chiller, it merges with condenser water flowing through a cooling tower.
Pumped Refrigerant
This method pumps chilled water through a heat exchanger and utilizes a cold pumped refrigerant to draw out the heat. The Pumped Refrigerant technique provides savings since it has the capacity to transmit energy from servers and it allows for humidification to be greatly reduced.
Indirect Air Evaporative System
With this technique, an air-duct that is connected to an indirect air evaporative cooler is utilized. This method is energy efficient and uses weather from the outdoors to cool the facility at times when it is cooler than the temperature inside. This air is used to add cooler air to the airflow within the data center.
Data Center Organization
Optimizing the organization and placement of your data center equipment is an easy and cost-efficient way to ensure that your data center is meeting the temperatures it needs to maintain productivity. Efficient organization for optimum data center temperatures includes hot/ cold aisle arrangement, containment, rack placement, cable organization, and usage of blanking panels.
Hot/ Cold Aisle Arrangement
Managing hot and cold aisles is a typical way to sustain temperatures in data centers. Without separating hot and cold aisles, the air within the data center will experience “mixing”, which is an inefficient use of energy. With air mixing, the equipment does not have the opportunity to be submerged in the optimal temperature that it needs to function. The hot/cold aisle method is implemented by positioning racks so that the lanes are divided by hot aisles and cold aisles.
Containment
Through the hot and cold aisles, containment can also be implemented to isolate the hot and cold air from the racks. When the containment is in use, the HVAC units can perform more efficiently. For this system, the hot air should be monitored to ensure that the hot aisle is not over-extended.
Rack Placement
The placement of the racks can minimize the heat circulation from rack hot spots. Within the rack, the hottest location is located at the top of the rack. To ensure optimal cooling, you can arrange your racks by organizing their components so that the heavier equipment is located on the lower racks. Since larger equipment circulates the most air, a lower rack placement will ensure that less hot air is dispersed at the top of the rack.
Cable Organization
Maintaining cable organization not only allows your cables to be neater and easier to manage, but it also ensures that the cables are not obstructing the data center’s airflow. It is a small step towards allowing your data center to optimize its airflow.
Blanking Panels
If your racks have unused space and your data center is not utilizing blanking panels, excess heat is being emitted into your data center’s airflow to accommodate rack space that is unoccupied. By using blanking panels, the hot air will be blocked from entering your data center’s airflow, proving greater cooling efficiency.
Environmental Monitoring
In addition to these techniques, it is important to be able to monitor and manage your facility in real-time. In order to ensure that your data center equipment is operating at the optimum temperature, environmental monitoring is important. With environmental sensors, you can monitor and manage your data center’s airflow, humidity levels, temperature, air pressure, and hotspots. More information about environmental monitoring can be found here.
Other Blog Posts
- Manage What You Measure: The Value of Legrand’s SmartSensor Portfolio
- Posted on June 20, 2024
- Data Centers are Getting Denser and Smarter: Here’s How Facility Managers Can Keep Up
- Posted on May 28, 2024
- How to Achieve Sustainability in Your Data Center Through Partnering
- Posted on May 16, 2024
- Who Should Care About ISO 27001?
- Posted on April 30, 2024
- The Rapid Growth of AI and the Use of Raritan PDUs to Meet Higher Power Demands
- Posted on October 11, 2023
Subscribe
Upcoming Events
Latest Raritan News
- Legrand Wins Back-to-Back Awards for Intelligent Rack Power Distribution Innovation
- Posted on May 24, 2024
- Legrand Certifications and Process Controls Provide Confidence in Information Security for Network-Connected Devices in Data-Related Applications
- Posted on April 1, 2024
- Legrand Releases Version 4.0 of Raritan’s Industry-Leading Secure KVM Switches, Raising Bar for Secure Desktop Access
- Posted on July 31, 2023
- Legrand Revitalizes Data Center Sector with Two Revolutionary Intelligent Rack PDUs
- Posted on May 1, 2023
- Raritan Reveals The MasterConsole® Digital Dual KVM Switch
- Posted on February 18, 2021